Other Uses: Shred the tender twigs for use as a toothbrush.
Saxaul
Haloxylon ammondendron

Description: The saxaul is found either as a small tree or as a large shrub with heavy, coarse wood and spongy, water-soaked bark. The branches of the young trees are vivid green and pendulous. The flowers are small and yellow.
Habitat and Distribution: The saxaul is found in desert and arid areas. It is found on the arid salt deserts of Central Asia, particularly in the Turkestan region and east of the Caspian Sea.
Edible Parts: The thick bark acts as a water-storage organ. You can get drinking water by pressing quantities of the bark. This plant is an important source of water in the arid regions in which it grows.
Screw pine
Pandanus species
Description: The screw pine is a strange plant on stilts, or prop roots, that support the plant above-ground so that it appears more or less suspended in midair. These plants are either shrubby or treelike, 3 to 9 meters tall, with stiff leaves having sawlike edges. The fruits are large, roughened balls resembling pineapples, but without the tuft of leaves at the end.

Habitat and Distribution: The screw pine is a tropical plant that grows in rain forests and semievergreen seasonal forests. It is found mainly along seashores, although certain kinds occur inland for some distance, from Madagascar to southern Asia and the islands of the southwestern Pacific. There are about 180 types.
Edible Parts: Knock the ripe fruit to the ground to separate the fruit segments from the hard outer covering. Chew the inner fleshy part. Cook fruit that is not fully ripe in an earth oven. Before cooking, wrap the whole fruit in banana leaves, breadfruit leaves, or any other suitable thick, leathery leaves. After cooking for about 2 hours, you can chew fruit segments like ripe fruit. Green fruit is inedible.
Sea orach
Atriplex halimus
Description: The sea orach is a sparingly branched herbaceous plant with small, gray-colored leaves up to 2.5 centimeters long. Sea orach resembles Iamb’s quarter, a common weed in most gardens in the United States. It produces its flowers in narrow, densely compacted spikes at the tips of its branches.
Habitat and Distribution: The sea orach is found in highly alkaline and salty areas along seashores from the Mediterranean countries to inland areas in North Africa and eastward to Turkey and central Siberia. Generally, it can be found in tropical scrub and thorn forests, steppes in temperate regions, and most desert scrub and waste areas.

Edible Parts: Its leaves are edible. In the areas where it grows, it has the healthy reputation of being one of the few native plants that can sustain man in times of want.
Sheep sorrel
Rumex acerosella

Description: These plants are seldom more than 30 centimeters tall. They have alternate leaves, often with arrowlike bases, very small flowers, and frequently reddish stems.
Habitat and Distribution: Look for these plants in old fields and other disturbed areas in North America and Europe.
Edible Parts: The plants are edible raw or cooked.
These plants contain oxalic acid that can be damaging if too many plants are eaten raw. Cooking seems to destroy the chemical.
Sorghum
Sorghum species
Description: There are many different kinds of sorghum, all of which bear grains in heads at the top of the plants. The grains are brown, white, red, or black. Sorghum is the main food crop in many parts of the world.
Habitat and Distribution: Sorghum is found worldwide, usually in warmer climates. All species are found in open, sunny areas.
Edible Parts: The grains are edible at any stage of development. When young, the grains are milky and edible raw. Boil the older grains. Sorghum is a nutritious food.
Other Uses: Use the stems of tall sorghum as building materials.

Spatterdock or yellow water lily
Nuphar species
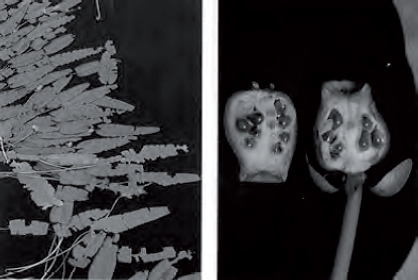
Description: This plant has leaves up to 60 centimeters long with a triangular notch at the base. The shape of the leaves is somewhat variable. The plant’s yellow flowers are 2.5 centimeter across and develop into bottle-shaped fruits. The fruits are green when ripe.
Habitat and Distribution: These plants grow throughout most of North America. They are found in quiet, fresh, shallow water (never deeper than 1.8 meters).
Edible Parts: All parts of the plant are edible. The fruits contain several dark brown seeds you can parch or roast and then grind into flour. The large rootstock contains starch. Dig it out of the mud, peel off the outside, and boil the flesh. Sometimes the rootstock contains large quantities of a very bitter compound. Boiling in several changes of water may remove the bitterness.
Sterculia
Sterculia foetida
Description: Sterculias are tall trees, rising in some instances to 30 meters. Their leaves are either undivided or palmately lobed. Their flowers are red or purple. The fruit of all sterculias is similar in aspect, with a red, segmented seedpod containing many edible black seeds.

Habitat and Distribution: There are over 100 species of sterculias distributed through all warm or tropical climates. They are mainly forest trees.
Edible Parts: The large, red pods produce a number of edible seeds. The seeds of all sterculias are edible and have a pleasant taste similar to cocoa. You can eat them like nuts, either raw or roasted.
Avoid eating large quantities. The seeds may have a laxative effect.
Strawberry
Fragaria species
Description: Strawberry is a small plant with a three-leaved growth pattern. It has small, white flowers usually produced during the spring. Its fruit is red and fleshy.
Habitat and Distribution: Strawberries are found in the North Temperate Zone and also in the high mountains of the southern Western Hemisphere. Strawberries prefer open, sunny areas. They are commonly planted.

Edible Parts: The fruit is edible fresh, cooked, or dried. Strawberries are a good source of vitamin C. You can also eat the plant’s leaves or dry them and make a tea with them.
Sugarcane
Saccharum officinarum
Description: This plant grows up to 4.5 meters tall. It is a grass and has grasslike leaves. Its green or reddish stems are swollen where the leaves grow. Cultivated sugarcane seldom flowers.

Habitat and Distribution: Look for sugarcane in fields. It grows only in the tropics (throughout the world). Because it is a crop, it is often found in large numbers.