Length: Average 45 centimeters, maximum 90 centimeters.
Distribution: Italy, Yugoslavia, northern Albania, and Romania.
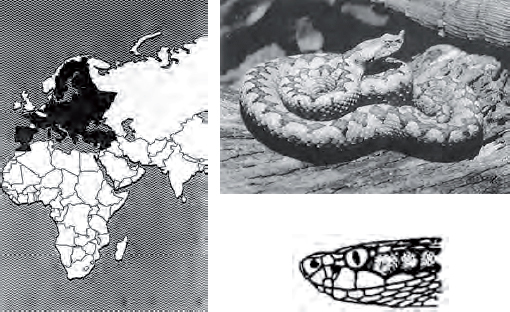
Pallas’ viper
Agkistrodon halys
Description: Coloration is gray, tan, or yellow, with markings similar to those of the American copperhead.
Characteristics: This snake is timid and rarely strikes. Its venom is hemotoxic but rarely fatal.
Habitat: Found in open fields, hillsides, and farming regions.
Length: Average 45 centimeters, maximum 90 centimeters.
Distribution: Throughout southeastern Europe.
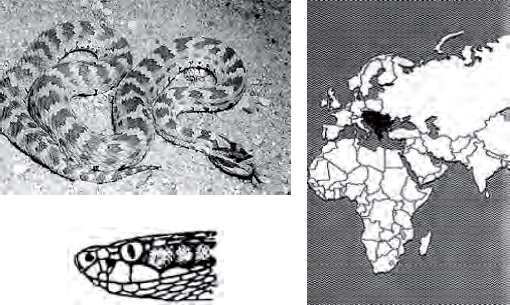
Ursini’s viper
Vipera ursinii
Description: The common adder, long-nosed adder, and Ursini’s viper basically have the same coloration and dorsal zigzag pattern. The exception among these adders is that the common adder and Ursini’s viper Iack the projection of tiny scales on the tip of the nose.
Characteristics: These little vipers have an irritable disposition. They will readily strike when approached. Their venom is hemotoxic. Although rare, deaths from the bites of these vipers have been recorded.
Habitat: Meadows, farmlands, rocky hillsides, and open, grassy fields.
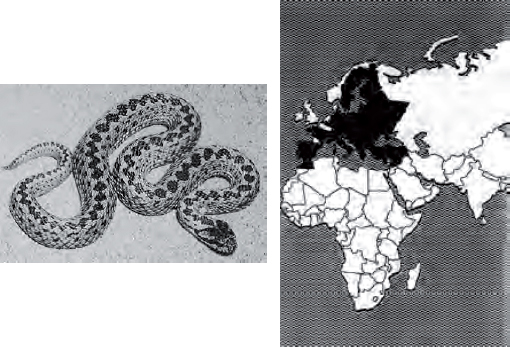
Length: Average 45 centimeters, maximum 90 centimeters.
Distribution: Most of Europe, Greece, Germany, Yugoslavia, France, Italy, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Albania.
POISONOUS SNAKES OF AFRICA AND ASIA
Boomslang
Dispholidus typus
Description: Coloration varies but is generally green or brown, which makes it very hard to see in its habitat.

Characteristics: Will strike if molested. Its venom is hemotoxic; even small amounts cause severe hemorrhaging, making it dangerous to man.
Habitat: Found in forested areas. It will spend most of its time in trees or looking for chameleons and other prey in bushes.
Length: Generally less than 60 centimeters.
Distribution: Found throughout sub-Saharan Africa.
Bush viper

Atheris squamiger
Description: Often called leaf viper, its color varies from ground colors of pale green to olive, brown, or rusty brown. It uses it prehensile tail to secure itself to branches.
Characteristics: An arboreal species that often comes down to the ground to feed on small rodents. It is not aggressive, but it will defend itself when molested or touched. Its venom is hemotoxic; healthy adults rarely die from its bite.
Habitat: Found in rain forests and woodlands bordering swamps and forests. Often found in trees, low-hanging branches, or brush.
Length: Average 45 centimeters, maximum 75 centimeters.
Distribution: Most of Africa, Angola, Cameroon, Uganda, Kenya, and Zaire.
Common cobra
Naja naja
Description: Also known as the Asiatic cobra. Usually slate gray to brown overall. The back of the hood may or may not have a pattern.
Characteristics: A very common species responsible for many deaths each year. When aroused or threatened, the cobra will lift its head off the ground and spread its hood, making it more menacing. Its venom is highly neurotoxic, causing respiratory paralysis with some tissue damage. The cobra would rather retreat if possible, but if escape is shut off, it will be a dangerous creature to deal with.

Habitat: Found in any habitat cultivated farms, swamps, open fields, and human dwelling where it searches for rodents.
Length: Average 1.2 meters, maximum 2.1 meters.
Distribution: All of Asia.
Egyptian cobra
Naja haje
Description: Yellowish, dark brown, or black uniform top with brown crossbands. Its head is sometimes black.

Characteristics: It is extremely dangerous. It is responsible for many human deaths. Once aroused or threatened, it will attack and continue the attack until it feels an escape is possible. Its venom is neurotoxic and much stronger than that of the common cobra. Its venom causes paralysis and death due to respiratory failure.
Habitat: Cultivated farmlands, open fields, and arid countrysides. It is often seen around homes searching for rodents.
Length: Average 1.5 meters, maximum 2.5 meters.
Distribution: Africa, Iraq, Syria, and Saudi Arabia.
Gaboon viper

Bitis gabonica
Description: Pink to brown with a vertebral series of elongated yellowish or light brown spots connected by hourglass-shaped markings on each side. It has a dark brown stripe behind each eye. This dangerous viper is almost invisible on the forest floor. A 1.8-meter-long Gaboon viper could weigh 16 kilograms.
Characteristics: The largest and heaviest of all true vipers, having a very large triangular head. It comes out in the evening to feed. Fortunately, it is not aggressive, but it will stand its ground if approached. It bites when molested or stepped on. Its fangs are enormous, often measuring 5 centimeters long. It injects a large amount of venom when it strikes. Its venom is neurotoxic and hemotoxic.
Habitat: Dense rain forests. Occasionally found in open country.
Length: Average 1.2 meters, maximum 1.8 meters.
Distribution: Most of Africa.
Green mamba
Dendraspis angusticeps
Description: Most mambas are uniformly bright green over their entire body. The black mamba, the largest of the species, is uniformly olive to black.

Characteristics: The mamba is the dreaded snake species of Africa. Treat it with great respect. It is considered one of the most dangerous snakes known. Not only is it highly venomous but it is aggressive and its victim has little chance to escape from a bite. Its venom is highly neurotoxic.
Habitat: Mambas are at home in brush, trees, and low-hanging branches looking for birds, a usual diet for this species.
Length: Average 1.8 meters, maximum 3.7 meters.
Distribution: Most of Africa.
Green tree pit viper
Trimeresurus gramineus
Description: Uniform bright or dull green with Iight yellow on the facial lips.
Characteristics: A small arboreal snake of some importance, though not considered a deadly species. It is a dangerous species because most of its bites occur in the head, shoulder, and neck areas. It seldom comes to the ground. It feeds on young birds, lizards, and tree frogs.