Wood Nettle
Laportea canadensis
Urticaceae family (Nettle family)

Occurrence: North America from Canada to Florida. Frequentlyfound in low forests and on riverbanks. The plant prefers grounds rich in nutrient.
Description: Up to 1.10 m high shrub with greenish blossoms, flowering from June to September. Parts above the ground are covered with stinging hairs. In contrast to the Stinging Nettle, leaves are alternate.
Effects: Mechanical-chemical through stinging hairs. After touching the plant burning and itching may occur, including reddening of the skin and perhaps blistering. Young leaves are edible when cooked.
Measures: Usually none. Sap from Impatiens or Rumex species can alleviate the effect. In more severe cases apply corticosteroid ointment, search medical attention, get Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference: Peterson
Tree Nettle
Laportea spp.
Urticaceae family (Nettle family)

Synonyms: Fever Nettle (en)
Occurrence: Frequently found in subtropical and tropical regions in Europe, Asia, and Australia. Also in secondary forests and thickets.
Description: Shrub or small tree with inconspicuous white or greenish blossoms. Leaves are covered with stinging hairs, mostly also leaf stalks and other parts.
Effects: Strong mechanical-chemical skin irritation by stinging hairs. After slightly touching the plant severe burning sensation or itching can occur. Later skin reddening and often blistering. Sleeplessness and fever can occur when large areas of the skin are affected.
Measures: Bath affected skin areas in soap solution. Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference: Merrill (1)
Nettle Tree
Urera baccifera
Urticaceae family (Nettle family)
Synonyms: Ortiga (es), Chichicaste (es)
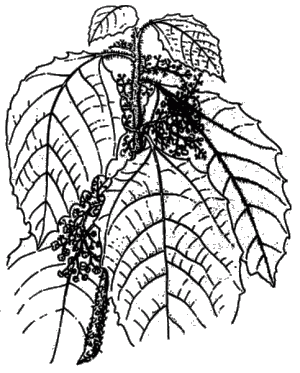
Occurrence: In tropical America frequently found at low and middle altitudes. Sometimes cultivated as hedge plants.
Description: Small bush, shrub or tree, covered with stinging hairs.
Effects: Severe mechanical-chemical skin irritation through stinging hairs. After slightly touching burninging sensation and itching. Later reddening and often blistering. Sleeplessness and fever can occur when extensive areas of the skin are affected. If leaves streak the body, this can already cause severe pain which can last for 24 hours.
Measures: Bath affected skin areas in a soap solution. Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference: Dahlgren
Stinging Nettle
Urtica dioica L.
Urticaceae family (Nettle family)

Synonyms: Common Nettle (en), Große Brennnessel (de)
Occurrence: These and other Urtica species are widespread world-wide on waysides, in margins of forests, in residential areas, and on rubble. In the tropics only at high altitudes.
Description: Up to 1.5 m high perennial shrub with an unbranched upright stem. Blossoms greenish, blooming period from July to October in the northern temperate zone. Parts above ground are covered with stinging hairs.
Effects: Mechanical-chemical through stinging hairs. After slightly touching the plant, burning sensation and itching may occur, including reddening of the skin and perhaps blistering. The young leaves are sometimes used as vegetables, the poisonous effect disappears after cooking.
Measures: Usually none. The sap of Rumex species (Sorrel, often found near to Stinging Nettles) can be used for alleviation. Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis in severe cases.
Reference: Roth; Benezra
Similar plants: Urtica urens (also called Stinging Nettle), appearance very similarly, but only up to 60 cm and annual. More than 500 other Urtica species world-wide.
Cashew Nut Tree
Anacardium occidentale L.
Anacardiaceae family (Sumac family)
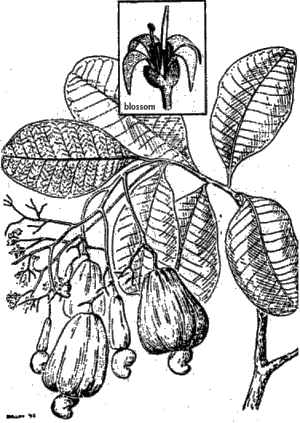
Synonyms: Kaschu (de), Acaju (es)
Occurrence: Resident in tropical America but also widespread in all other tropical countries because the nuts are cultivated. This tree prefers dry ground and is usually not found in forests.
Description: Evergreen tree up to 10 m tall with leathery leaves, white blossoms with pink stripes and a fruit which consists of two parts: The upper part (the Cashew apple) is red, yellow or white and contains white edible pulp (tasting sweet and slightly peppery). The lower part of the fruit is grey and very skin-irritating. It contains the Cashew nut which is edible only after being roasted.
Effects: Chemically skin-irritating and allergizing. The plant's sap from bark, leaves and particularly the nutshell can within one day cause painful skin alterations which resemble second-degree burns. This sap is brown and oily and becomes black when exposed to the air. The fumes which emerge from roasting the nuts are skin-irritating and can even lead to blindness.
Measures: Take extreme caution when harvesting nuts or fruits and also when roasting the nuts. Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference: Benezra; Behl; Roth; Dahlgren
Rengas
Gluta renghas L.
Anacardiaceae family (Sumac family)

Occurrence: South-East Asia and India.
Description: Tree.
Effects: Allergizing and chemically skin-irritating. The smoke of the burning wood can also be dangerous.
Measures: Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Holigarna
Holigarna arnottiana Hook.f.
Anacardiaceae family (Sumac family)

Occurrence: Western India in evergreen forests.
Description: Tall tree, the treetop being closely covered with leaves. Leaves are large and hairless. Fleshy, oval stone fruits (drupes) in clusters. Small blossoms.
Effects: Allergizing and chemically skin-irritating. The smoke of the burning wood can also be dangerous.
Measures: Corticosteroid ointment, medical attention, Tetanus prophylaxis.
Reference: Behl
Similar plants: Melanochyla und Campnosperma act similar; they are found in the Indo-Malaysian area.